Executive Summary
For July’s Patch Tuesday round-up, there were 143 security updates from Microsoft. Of the updates, a majority of the vulnerabilities are categorized as Remote-Code-Execution (RCE), followed by privilege elevation (with one exploited in the wild), and security feature bypasses. On the lower end, information disclosure and spoofing issues were also within July’s Patch Tuesday (with one spoofing vulnerability being actively exploited in the wild). Aside from the two issues that were exploited in the wild, Microsoft categorizes fourteen as “Exploitation More Likely”.
Key Details
- Following the average, at least two of the patched items for this month are known to be actively exploited in the wild. Targeting Windows core services and browser based exploits are still favored amongst threat actors and researchers alike.
- An update to CVE-2023-24932(security feature bypass of Secure Boot abused to serve Black Lotus malware in the past) was also included in this update, as well as several new Security Feature Bypass issues within Secure Boot (most of them requiring user interaction).
- A majority of the high severity findings involve SQL server’s Native Client due to heap-based overflow vulnerabilities.
ANALYST COMMENTS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Two vulnerabilities were found to be exploited in the wild that take advantage of MSHTML (a component of Internet Explorer) and an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Windows Hyper-v. These vulnerabilities are both in line with current tactics employed by threat actors and it is likely that more utilitarian vulnerabilities such as spoofing and privilege elevation issues will continue to be favored. Particularly, by threat actors serving ransomware for financial gain and nation-state sponsored actors conducting espionage campaigns for the purposes of planting trojans and backdoors. Given how effective phishing and social engineering campaigns are, this is another reason threat actors tend to favor these types of issues.
While SQL server had the largest number of high-rated vulnerabilities associated with it this month, Secure Boot was also the target of several CVEs. While a majority of these issues require user interaction, along with Lan or physical access to these machines, it is not an unprecedented route for malware to be served by an attacker that is within the network or a malicious insider. A survey of 467 security professionals, conducted by Cybersecurity Insiders would suggest that the insider threat has grown since 2019 to 2024 which could likely be attributed to elevated detection rates of malware within internal network environments. Given this, it’s recommended that companies adopt a zero trust model within their organization, as in the event of an internal compromise or suspicious activity, to minimize potential damage and impact.
It is always recommended that any and all security patches be applied within their respective environments. However, it is recommended that issues that have been exploited in the wild are given priority, along with issues that carry or will be suspected to have a public PoC released within its lifecycle, and issues that are known to be critical or high risk. Social engineering is still the preferred vector of attack for most threat actors, utilizing phishing, masquerading as tech support persons, and so on. Therefore it’s important to have regular security awareness training to ensure that employees are able to spot suspicious communications before an incident occurs.
Exploited in the Wild
This section details the vulnerabilities that have been known to be abused in the wild. These issues should be taken care to be remediated within the environment as known exploitation has taken place and organizations should take especial care in ensuring these items are mitigated within their environment.
For this month, two of the newly released vulnerabilities are known to be exploited in the wild. It should be noted that this can change over time, especially for issues with known publicly available code or research available.
CVE-2024-38112 – Windows MSHTML Platform Spoofing Vulnerability
This is a spoofing vulnerability within the Windows MSHTML platform that can be abused with a specially crafted HTML file. MSHTML is a component of Internet Explorer and the issue does not result in direct compromise of any associated asset, as it is a more “utility” vulnerability that would be (and has) been used in a longer attack chain. Abuse would involve a malicious actor sending the crafted HTML file to an unsuspecting victim and convincing them to open the file in order to trigger exploitation. Currently there is no known PoC that is publicly available. This issue affects multiple versions of Windows 10, 11, and server deployments from 2008 to 2022.
CVE-2024-38080 – Windows Hyper-V Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
The vulnerability exists in multiple versions of Windows Hyper-V. Microsoft has reported this as being exploited in the wild. As of writing, there is currently no public exploit available. An authenticated local attacker can exploit this vulnerability to gain SYSTEM privileges on the system. We strongly recommend that all affected systems be updated immediately.
| CVE | Title | CVSS | CWE | MITRE MAPPING | Urgency | Issue Class | Product Class |
| CVE-2024-38112 | Windows MSHTML Platform Spoofing Vulnerability | 7.5 | CWE-668 | T1574 T1656 |
HIGH | Spoofing | Internet Explorer |
| CVE-2024-38080 | Windows Hyper-V Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 7.8 | CWE-190 | T1068 | HIGH | Elevation of Privilege | Windows Hyper-V |
MOST LIKELY TO BE EXPLOITED
This section details the vulnerabilities that OSec deems likely to be exploited in the wild at some point in the future, given past vulnerabilities or similar types under active exploitation. These issues should take care to be remediated within the environment as these vulnerabilities are more likely over others to be exploited by threat actors in the wild and carry a High or Critical level of urgency.
CVE-2024-38023 – Microsoft SharePoint Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
This vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint Server allows an authenticated attacker with Site Owner permissions or higher to upload a specially crafted file and trigger deserialization of the file’s parameters via an API request. This results in remote code execution in the context of the SharePoint server. This affects Microsoft SharePoint Server Subscription Edition, Microsoft SharePoint Server 2019, and Microsoft SharePoint Enterprise Server 2016.
CVE-2024-38060 – Windows Imaging Component Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
This is a heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability in Windows Imaging Component. The Windows Imaging Component is a native codec framework in Windows OS that processes images and image metadata. An attacker would upload a specially crafted Tag Image File Format (TIFF) file to the target system. When the target system attempts to process the image it would result in remote code execution. This affects Windows 10 and 11, Windows Server 2008, 2012, 2016, 2019, and 2022.
CVE-2024-38021 – Microsoft Office/Outlook Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
This vulnerability is a critical zero-click input validation bug in Microsoft Office and Outlook. As this is a zero-click vulnerability, it requires no user interaction and triggering of this vulnerability could result in execution of remote code and compromise of the affected account and device. However, it should be noted that the zero-click nature only applies to “trusted senders” and that emails coming from untrusted senders would still require a 1-click from the victim in order to trigger the vulnerability. The researchers responsible for finding this issue will reportedly present their findings on this issue in August during Defcon 32 and should be assumed that after said date, a public PoC may be available to take advantage of this issue. This affects Office 365 and local versions between 2016 and 2021.
CVE-2024-28899 – Secure Boot Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
A stack overflow exists that bypasses the security features of Secure Boot. While this issue would require prior conditions being met prior to exploitation, security bypasses of Secure Boot is not an unprecedented attack vector, such as the case for a former Secure Boot vulnerability from last year serving Back Lotus malware. Bypassing secure boot can result in loading of malicious .wim (Windows image) files leading to remote code execution should the attacker have Lan or physical access to the vulnerable computer. This issue affects Windows versions 10,11 and server deployments between 2012 and 2022.
| CVE | Title | CVSS | CWE | MITRE MAPPING | Urgency | Issue Class | Product Class |
| CVE-2024-38023 | Microsoft SharePoint Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
|
7.2 | CWE-502 | T1210 | CRITICAL | Remote Code Execution | Microsoft SharePoint Server |
| CVE-2024-38060 | Windows Imaging Component Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 8.8 | CWE-122 | T1210 | CRITICAL | Remote Code Execution | Windows OS |
| CVE-2024-38021 | Microsoft Office/Outlook Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 8.8 | CWE-20 | T1210 | CRITICAL | Remote Code Execution | Microsoft Office |
| CVE-2024-28899 | Secure Boot Security Feature Bypass | 8.8 | CWE-121 | T1553
T1195 |
HIGH | Remote Code Execution | Secure Boot |
Year to Date Trends
The following trends have been observed over the last 7 months in regards to issues with known PoCs or known to be exploited in the wild. From February to July of 2024 there are currently 20 known publicly available PoCs or research and 16 known issues to have been abused by threat actors.
Microsoft Windows core services and browser based vulnerabilities have the highest amount of PoCs and known abuse by threat actors. Privilege escalation and security bypass issues are also the most exploited vulnerability type by threat actors. Privilege elevation in Windows applications and services will likely continue to grow along the same pace it has been this year, along with more security bypass issues. Additionally, it is likely that spoofing will continue to grow, along with more exploitation targeting Microsoft Office products, specifically Outlook as phishing related tactics are still a favorite for initial breaches by threat actors, along with using stolen credentials.
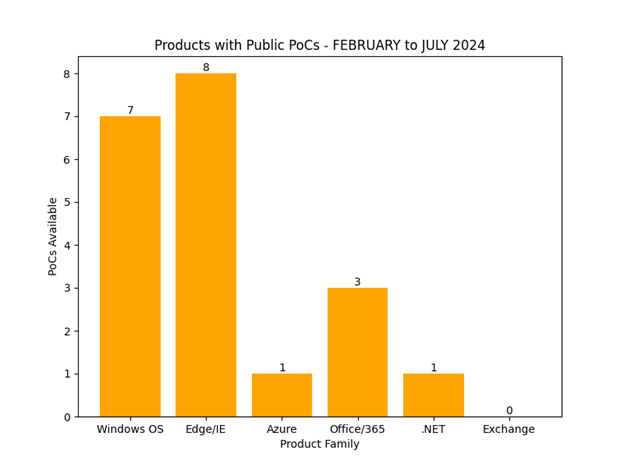
Figure 1 – Not much change from last month, only one new PoC added for Office/365
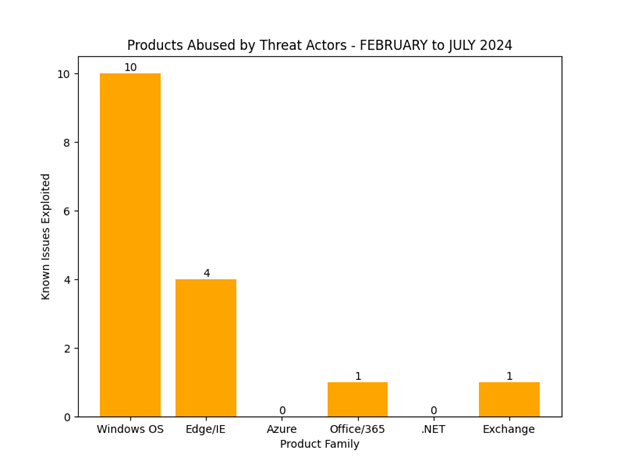
Figure 2 – Also not much change with the newest additions in Windows OS and Edge/IE categories
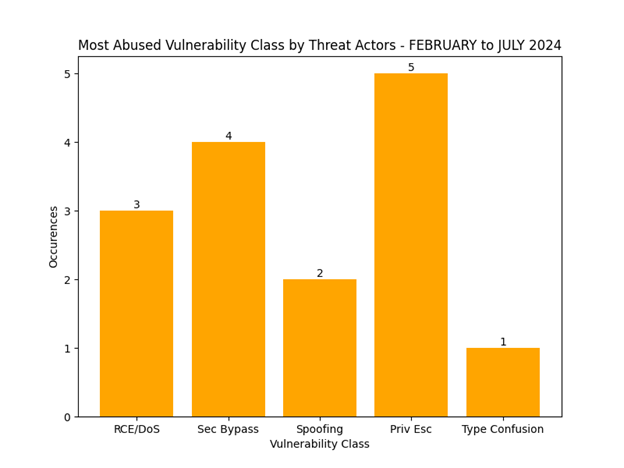
Figure 3 – Only two items added this month to Spoofing and Privilege Escalation categories
References
Bleeping Computer – Microsoft Patch Tuesday Fixes…
https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/microsoft/microsoft-july-2024-patch-tuesday-fixes-142-flaws-4-zero-days/
Microsoft Vulnerability Update Guide
https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/vulnerability
4sysops – New Mitigations for Black Lotus…
https://4sysops.com/archives/new-mitigations-for-cve-2023-24932-blacklotus-in-the-april-update-not-yet-enabled-by-default/
MORPHISEC – CVE-2024-38021
https://blog.morphisec.com/cve-2024-38021-microsoft-outlook-moniker-rce-vulnerability
Cybersecurity Insiders – 2024 Insider Threat Report
https://www.securonix.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/2024-Insider-Threat-Report-Securonix-final.pdf