Introduction
In today’s complex IT landscape, organizations are inundated with a growing volume of vulnerabilities. Effective management of these vulnerabilities is crucial for maintaining the resilience of the organization and ensuring the continuity of daily operations. Tagging, a powerful feature already built into Incenter, offers an advanced way to streamline vulnerability management by allowing users to assign custom or predefined tags to assets. By filtering vulnerability information based on these tags, organizations can significantly improve their security posture.
Understanding the Power of Tagging
Tagging assets with vulnerabilities in Incenter offers several key advantages that enhance both efficiency and security:
1. Improved Efficiency and Productivity
- Focused Vulnerability Assessment: By grouping assets based on tags, security teams can prioritize vulnerabilities according to specific criteria such as data classification, department, or environment. This targeted approach saves time and resources by enabling security teams and decision-makers to concentrate on the most critical issues.
- Accelerated Remediation: Tagging enables organizations to quickly identify assets that require immediate attention, such as those handling sensitive data or belonging to critical departments. This facilitates rapid remediation and reduces the risk of exploitation.
2. Enhanced Risk Management
- Risk-Based Prioritization: Tagging helps categorize assets based on their associated risk-based tags. This allows organizations to allocate resources effectively and prioritize remediation efforts accordingly.
- Compliance Adherence: By tagging assets based on data classification and department, organizations can demonstrate compliance with industry regulations and internal policies. This structured approach provides focus and direction, ensuring that all necessary vulnerabilities are addressed for compliance audits.
3. Improved Collaboration and Communication
- Shared Language: Tagging provides common terminology for security teams, developers, and other stakeholders to discuss and prioritize vulnerabilities. This shared language helps maintain consistency and clarity across the organization.
- Effective Communication: By using tags, organizations can easily communicate vulnerability information and status to relevant parties, such as department heads or business owners, ensuring that everyone is informed and aligned.
Leveraging Tagging in the UI
The implemented tagging functionality in Incenter plays a crucial role in supporting and significantly enhancing vulnerability management efficiency. Key features include:
- Intuitive Tag Creation and Management: The user interface (UI) allows users to easily create, edit, and delete tags, as well as organize groups of tags through the use of categories. This makes managing large sets of assets more straightforward and adaptable to various organizational needs.
- Flexible Tag Application: Assets can be associated with multiple tags across various categories. Given that different users or audiences may have distinct perspectives, the ability to assign multiple tags to a single asset ensures that assets can be viewed and managed according to different contexts.
- Dynamic Filtering: The UI supports multiple tag/category filtering, which helps provide focus on the vulnerabilities and weaknesses identified in the environment. This dynamic filtering capability allows teams to drill down into specific areas of concern and address them more efficiently.
Tagging in action
Best Practices for Tagging
To maximize the benefits of tagging in Incenter, consider the following best practices:
- Standardize Tagging Terminology: While the system provides default categories and tags based on established industry terminology, it is important that organizations establish clear definitions and guidelines for tag usage to ensure consistency across the organization.
- Regular Tag Review: Periodically reviewing and updating tags and categories according to organizational needs and changes is crucial for maintaining accuracy and relevance. This ensures that the tagging system evolves with the organization.
- Involve Stakeholders: Collaborate with different departments to identify relevant tags and ensure their needs are met. This collaborative approach ensures that the tagging system is comprehensive and reflects the diverse needs of the organization.
Conclusion
Tag filtering is a powerful function that enhances asset management and vulnerability tracking within Incenter. With effective utilization of the tagging function, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture, improve efficiency, and make more informed decisions. Ultimately, by providing context driven direction, the tagging function aims to help alleviate the strain on limited resources, personnel, and budget, ensuring that even with constraints, security objectives are effectively met.
Real-World Applications of Tagging: Case Studies
To illustrate the practical benefits of the tagging function within Incenter, below are two real-world use cases from organizations that have successfully integrated tagging into their cybersecurity strategies.
Use Case 1: Asset Type-Based Tagging
This organization operates within a complex IT environment where different teams manage various types of assets. To streamline their vulnerability management process, they have implemented the following approach:
- Tagging by Asset Type: Each asset within the organization is tagged based on its type, such as servers, workstations, or network devices. These tags are closely aligned with the teams responsible for managing these assets.

Tag Configuration by Asset Type
- Team-Based Asset Management: Since asset types are managed by different teams, the tagging system ensures that each team has a clear view of the vulnerabilities associated with the assets they are responsible for.

Tag Filter by ‘Servers’ Tag
- Vulnerability Management: By managing vulnerabilities through asset-type tags, this organization can prioritize remediation efforts based on the criticality of the asset type, ensuring that the most vital assets are secured first.
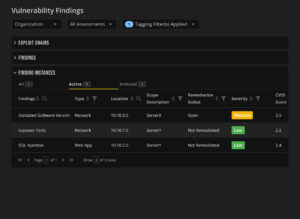
Updated Vulnerability Findings for Applied ‘Servers’ Tag
Use Case 2: Geographic Location-Based Tagging
Another organization has a global footprint with multiple physical locations, each managed by the corporate security team. Their tagging strategy is designed to address the unique challenges of managing security across geographically dispersed sites:
- Tagging by Geographic Location: The organization applies tags to assets based on their geographic location, such as North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Middle East. This geographic tagging helps the corporate security team maintain a clear overview of vulnerabilities across all locations.
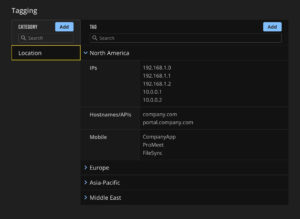
Tag Configuration by Location
- Location-Based Vulnerability Management: Vulnerabilities are managed based on site location, allowing the corporate security team to quickly identify and address threats specific to each region. This is particularly useful for responding to region-specific threats or compliance requirements.

Tag Filter by ‘North America’ Tag
- Local Responsibility for Remediation: While the corporate security team oversees the overall strategy, local managers at each site are responsible for remediating issues. The tagging system ensures that local managers have the necessary visibility into their specific vulnerabilities, empowering them to take timely action.
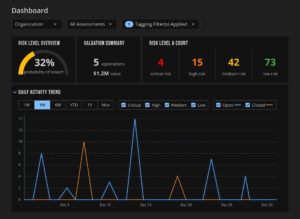
Updated Dashboard for ‘North America’ Tag